How to protect your crypto from hackers

The crypto winter and market disruptions of 2022, including the fallout of some algorithmic stable coin issuers and major exchanges, have shaken investors’ sentiment toward the safety of cryptocurrency investments.
The ongoing threat of cyber-attacks and multiple scams makes crypto security a top priority for traders and investors. So how can crypto holders ensure their assets are safe?
Let’s dive deep into the major crypto security risks as we head into 2023 and elaborate on how to protect your cryptocurrency from hackers.
Top crypto hacks in 2022: DeFi as the primary target
2022 was a record year for crypto hackers. As of October, they had stolen over $3 billion through 125 hacks, according to Chainalysis. October alone became the biggest month ever for hacking activity, with $718 million wiped from DeFi protocols.
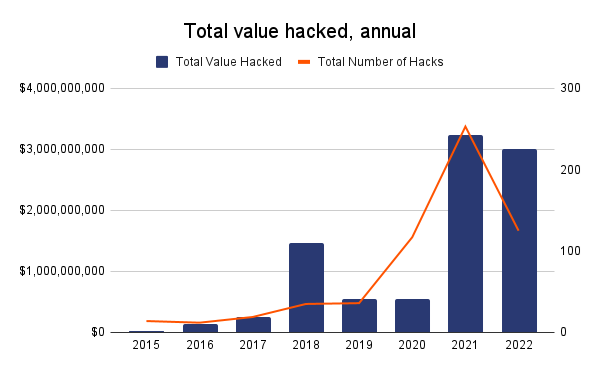
Source: Chainalysis, as of October 2022
Notoriously, cryptocurrency hackers have changed their targets. Back in 2019, most attacks hit centralized crypto exchanges, while decentralized finance apps have now taken the lead.
In 2022, almost 90% of all cyber-attacks targeted DeFi protocols and cross-chain bridges.
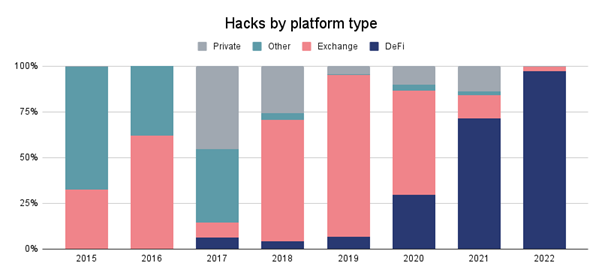
Source: Chainalysis, as of October 2022
What are the biggest crypto hacks in 2022? Let’s view several high-profile cyber-attacks on cryptocurrency blockchains that have occurred recently.
Top 5 crypto hacks in 2022
1. Ronin Network: $625 million
The Ronin network is an Ethereum-linked sidechain that was created specifically for blockchain games. In March 2022, a hacker stole 173,600 Ether (ETH) and 25.5 million USDC – with a combined value of $625 million at the time – from Axie Infinity’s Ronin Network.
2. FTX exchange: $477 million
In November 2022, a hacker stole $477 million worth of tokens from FTX exchange, following its collapse earlier the same month. Although it has yet to be determined, it is possible that the hack was carried out by an insider.
3. Wormhole Bridge: $325 million
In February 2022, The Wormhole token bridge, which enables token transfer between Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon, Solana, and Avalanche, lost 120,000 Wrapped Ether (WETH) worth approximately $325 million at the time of the attack.
4. Nomad Bridge: $190 million
In August 2022, Nomad, a cross-chain bridge used for swapping tokens between Ethereum, Avalanche, Evmos, Milkomeda C1, and Moonbeamfell, victim to a security exploit and lost almost all its funds. More than $190 million vanished from the platform.
5. Beanstalk Farms: $182 million
In April 2022, Beanstalk Farms, an Ethereum-based stablecoin protocol, lost $182 million in total value locked (TVL) after an exploit in the protocol’s governance system.
Major cybersecurity risks explained
How do hackers steal crypto? To avoid first-hand experience with losing your money due to the malicious actions of hackers and crypto scammers, it’s worth learning the core blockchain cybersecurity risks and pain points they use.
-
Blockchain network attack
Blockchain consists of nodes or network participants that run and validate transactions. Cybercriminals identify the blockchain network’s vulnerabilities and exploit them using multiple types of attacks, including distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, transaction malleability attack, and timejacking.
-
User wallet attack
User wallet credentials remain one of the most significant crypto cybersecurity pain points. People overestimate blockchain security and forget about personal security measures. Meanwhile, hackers use various techniques to obtain user wallet credentials, including phishing, vulnerable signatures, flawed key generation, and attacks on cold and hot digital wallets.
-
Smart contract attack
Smart contracts also suffer from cryptocurrency hacks. Core cybersecurity issues associated with smart contracts involve bugs in source code, a network’s virtual machine, or the runtime environment - a layer utilized for smart contract execution and preserving the state between executions.
-
Transaction verification mechanism attack
Unlike traditional financial institutions, blockchains confirm transactions only after the majority of nodes reach a consensus. As the verification process can take time, it can create vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Double spending is a widespread blockchain attack in which the same amount can be spent twice in different transactions.
Examples of double-spending attacks include the “Finney attack”, the “race Attack, vector76, and “51% attack”.
-
Mining pool attack
Miners combine their computing power into mining pools to produce more blocks and get a share of the block reward, a reward given in crypto to a miner for successfully solving a complex mathematical problem and adding a new block to the blockchain. In a mining pool attack a group of miners, or a single miner with a significant amount of computational power, attempts to gain control of the network by controlling more than 50% of the network's mining power (also called hash rate). Examples of mining pool attacks are selfish mining and fork after withholding (FAW).
Although blockchains implement robust security measures, even the top networks might come under cyberattack.
Deloitte's Blockchain and Cybersecurity report states, "No cyber defense or information system can be regarded as 100% secure. What is deemed safe today won't be tomorrow given the lucrative nature of cybercrime and the criminal's ingenuity to seek new methods of attack".
Even though you can't personally prevent network-large security breaches, you can implement the best personal security practices to mitigate the risk of becoming a victim of cybercriminals.
How to secure your cryptocurrency? 5 best practices
Craig Goodwin, Co-founder and CEO of Bleach Cyber, said to XBO.com: “Using reputable retailers of crypto as well as reputable wallets is a must. We've seen recently that this isn’t always fool proof; however, it will give you the best shot at ensuring that the tools you use are backed by security best practices. Personal security hygiene is also important – password administration, multi-factor authentication on all accounts, and running software updates are a few.”
So, how to protect crypto from hackers? We have compiled a step-by-step security guide to help you safeguard your funds.
1. Trade on reputable exchanges
There are over 500 cryptocurrency exchanges available today, of which dozens have multi-billion trading volumes.
Although the size of the crypto exchange doesn't prove their security, it usually means they have solid cybersecurity infrastructures and store users' crypto assets at heavily surveilled and geographically distributed dedicated facilities.
While choosing a crypto exchange for trading and investments, consider if they provide sufficient security measures, such as two-factor authentication or biometric login, besides checking the coins' availability and liquidity, as well as comparing fees.
2. Store your crypto assets in multiple crypto wallets
How you store your crypto holdings depends on your activity as an investor or trader. For example, if you’re an active trader, you need a specific amount of funds promptly available anytime you want to trade. In this case, keeping your crypto holdings on an account at a crypto exchange might be a reasonable solution.
However, keeping large sums in a crypto account or a “hot wallet” (connected to the Internet) is dangerous from a cybersecurity perspective. Despite all the protection measures, breaches do happen. Besides, some crypto platforms might halt withdrawals – which means you will not be able to take your funds from the exchange for some time – during flash crashes and severe market downturns.
If you have a significant amount of crypto you’re going to hold for a long time, you can consider storing it in multiple wallets, especially hardware wallets, known as “cold wallets”. The significant difference between cold and hot wallets is that cold wallets are stored offline, i.e., are unavailable to hackers.
Self-custody gives you complete control over your private keys and tokens. However, when setting up your cold storage, you take full responsibility for safeguarding your private keys.
3. Beware of scams
The more cryptocurrencies go mainstream, attracting billions of dollars, the more crypto-related crime emerges. Gurvais Grigg, Global Public Sector Chief Technology Officer at Chainalysis, said: “You can’t have trillions of dollars move into a new asset class and not attract criminals, grifters, and malign actors.”
Scams have become the most prominent form of cryptocurrency-related crime, with more than $26 billion stolen between 2017 and 2021.
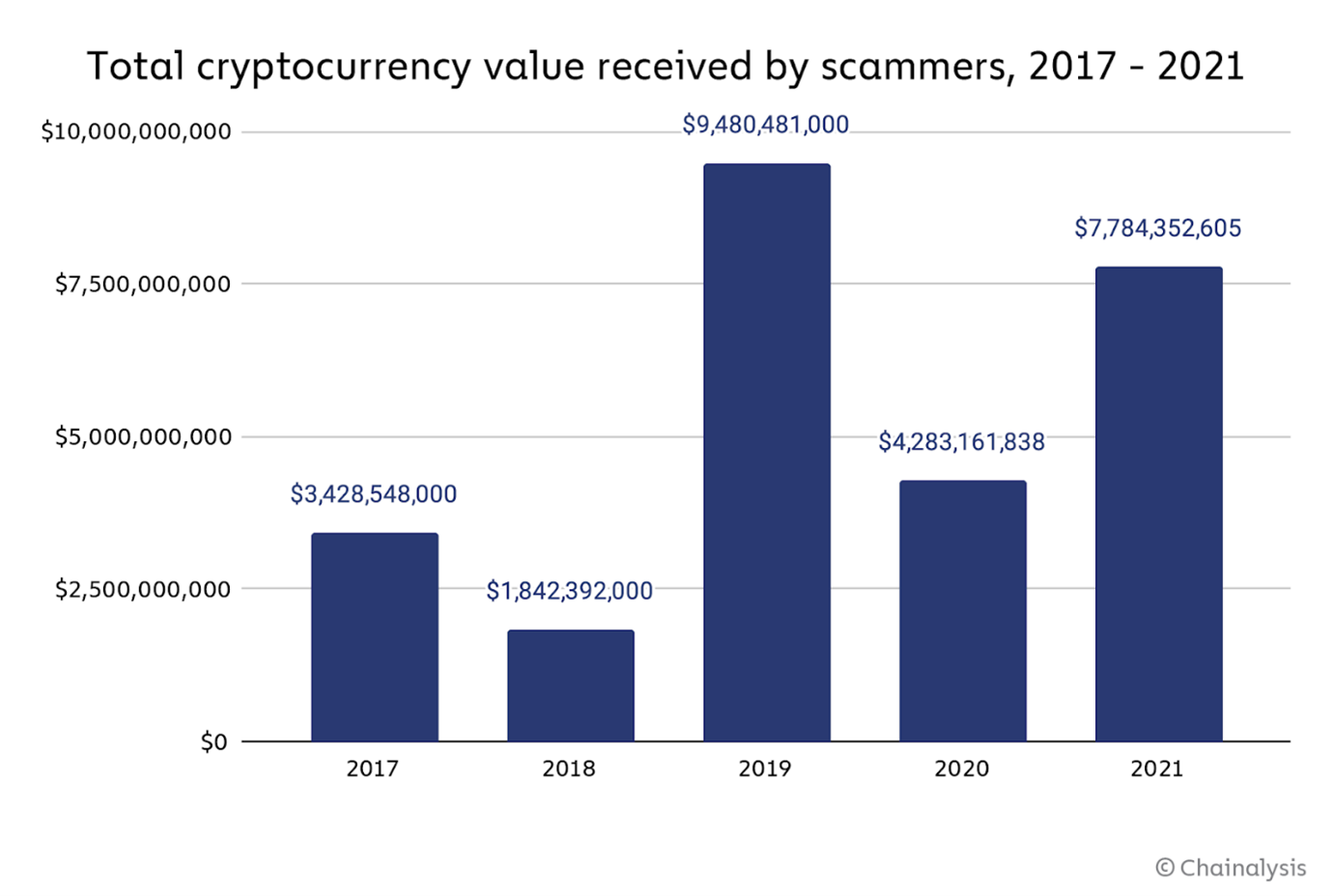
Source: Chainalysis
There are various types of crypto scams, from Ponzi schemes and rug-pulls to promoting fake crypto giveaways and setting up fake, fraudulent crypto websites. Furthermore, sophisticated phishing attacks that trick people into disclosing sensitive information are still common.
To protect your crypto from scammers, ensure you do not click on suspicious links, stay cautious about giveaways on social media, avoid advertisements on search engines, and check the URLs you enter.
4. Use a secure internet connection
Another valuable practice is to set up a secure cyber environment, which starts with a safe internet connection. However, it goes beyond avoiding public Wi-Fi and avoiding suspicious websites.
If you trade or invest in crypto mostly from home, you can check if your antivirus software is up-to-date and test your firewall for weaknesses. Then, you can set a strong password for your router, enable network encryption, and disable network name broadcasting.
As an additional security layer, consider using a virtual private network (VPN) solution, which can help to hide your activity from potential criminals.
5. Use multiple passwords and two-factor authentication
Using the same password on multiple resources is a no-go. It is actually the worst thing you can do for your online security.
According to Microsoft's Digital Defence Report 2022, the volume of password attacks has surged to 921 attacks every second – a 74% rise in just one year.
If you want to protect your crypto assets, always use complex, unique passwords and change them regularly. If you struggle remembering your multiple passwords, consider using a password management tool instead of keeping the list of your passwords as a text doc on your computer. Speaking of private keys to your crypto assets, consider storing them on an external device, such as a USB.
Most crypto exchanges today, including XBO.com, implement two- or multi-factor authentication, which adds another security layer to your crypto account.
Cybersecurity in the crypto world: shared responsibility
Are there any positive signs that financial organizations and crypto holders can cope with evolving cybersecurity threats? In an interview with Executive Mosaic, Grigg said that the total illicit activity involving crypto increased dramatically in 2022. However, the percentage or share of illegal activity vs. the overall crypto market cap has dropped.
This could be encouraging for consumers. While more people are entering the space and more money is moving into it, the actual share of illicit activity is diminishing. That means financial institutions worldwide excel at identifying and preventing scams and cyber attacks.
Nevertheless, the $14 billion worth in illicit activity, which Chainalysis identified in 2022, is a sizeable amount, which makes investors and traders concerned.
Speaking of primary security factors to consider while choosing a safe crypto storage option – a wallet or a centralized/decentralized exchange account – Goodwin concludes:
"Make sure you are using a reputable business. It's not always the case, as we've seen from recent events; however, the larger and more reputable the business, the more money they have to spend on security controls. That said, there is always a shared responsibility for security, and you must do your part (as listed above)."
FAQs
Can you recover stolen crypto?
If someone has stolen your cryptocurrency assets, it's probably gone for good. The odds of recovery are, unfortunately, not in your favor.
Theoretically, as the assets are transferred and registered on a blockchain, it is possible to track their movements. There are numerous services, like ReportScammedBitcoin.com, that work with law enforcement agencies and crypto holders to search for and regain access to lost or stolen cryptocurrencies.
What are the signs of fake cryptocurrencies?
There are several warning signs that should make you cautious:
- Promises of guaranteed returns
- Non-existent or poor whitepaper
- Excessive marketing
- Unknown team members
- Free money offering
How to identify cryptocurrency scams?
Conduct thorough research on every project you are considering investing in. Review the project’s whitepaper, security audits (if available), the team, and the company’s registration and compliance data.
Avoid crypto projects, promising big returns in a short time. Always remember that trading and investing in crypto is risky, and you can lose your money.




